Blogs

Palo Alto Networks To Buy CyberArk For $25 Billion
July 30, 2025
Best AI Tools for Affiliate Marketers: Boost Your Earnings with Smart Tech
August 1, 2025The role of server software cannot be overstated. From serving websites and managing emails to powering enterprise applications and storing vast amounts of data, server software is the backbone of most modern IT infrastructures. Whether you’re setting up a simple server for personal use or managing a complex data center for a large organization, understanding server software is key to ensuring the performance, security, and reliability of your systems.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of server software, covering the essential concepts, types, popular solutions, and best practices to help you navigate the world of server management.
Server Software: The Ultimate Guide
What is Server Software?
Server software is a program or application that runs on a server, allowing it to handle specific tasks and services requested by clients or users over a network. Unlike desktop software, which runs on personal computers, server software is designed to run continuously and handle multiple client requests simultaneously. Server software can be used for a wide range of functions, including hosting websites, managing databases, handling emails, and much more.
At its core, server software enables communication between the server and its clients (usually end-users or other servers), allowing users to access shared resources, data, or services from anywhere in the world.
Types of Server Software
Server software can be categorized into several different types based on its functionality. Below are some of the most common types:
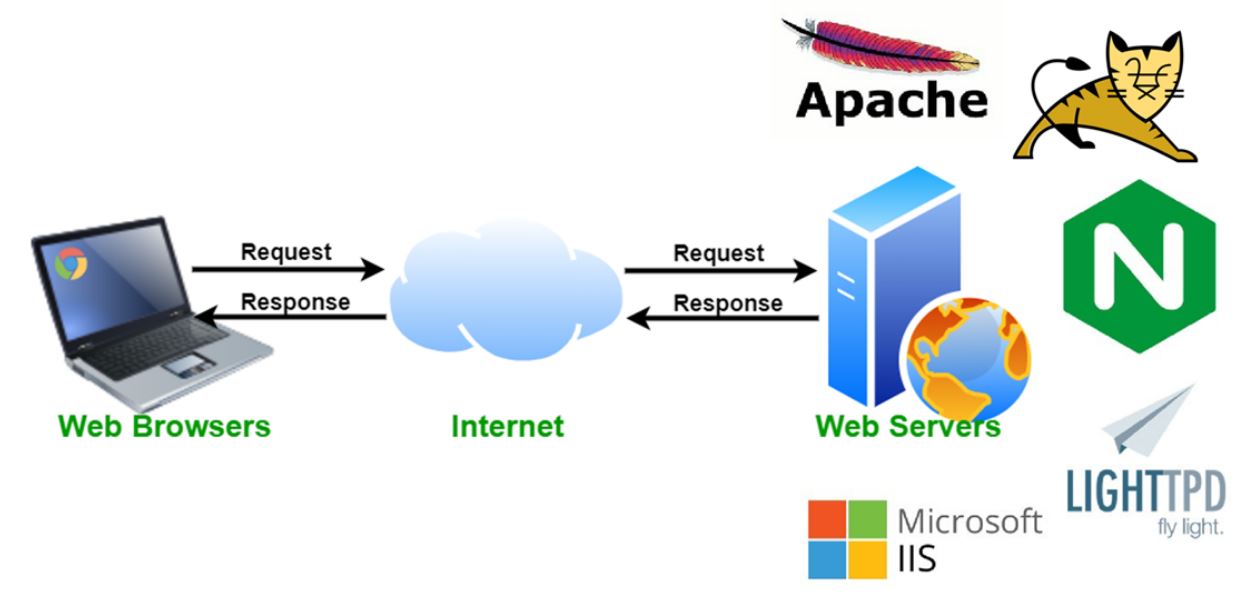
1. Web Server
Web servers are among the most widely used types of server software, playing a crucial role in website development and online content delivery. They are responsible for delivering web pages to clients (web browsers) over the internet. When a user requests a website, the web server processes the request, retrieves the appropriate files, and sends them back to the client. Web server software is typically optimized for high-volume traffic and fast delivery of content
Popular Web Servers:
- Apache HTTP Server: One of the oldest and most widely used web servers. It’s open-source, highly customizable, and runs on many operating systems.
- NGINX: Known for its high performance and low resource consumption, NGINX is used by many high-traffic websites.
- Microsoft IIS (Internet Information Services): A web server for Windows Server, offering deep integration with Microsoft technologies like ASP.NET.
2. Database Server
A database server is a system that stores, retrieves, and manages databases for clients. It is used to handle large amounts of data, such as user profiles, inventory records, transaction histories, and more. Database server software provides the necessary tools to efficiently store and manage data, ensuring high availability, security, and performance.
Popular Database Servers:
- MySQL: An open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) widely used for web applications.
- PostgreSQL: Known for its robustness and advanced features, PostgreSQL is an open-source RDBMS.
- Microsoft SQL Server: A relational database server developed by Microsoft, commonly used for enterprise applications.
- Oracle Database: A high-performance, enterprise-grade RDBMS that offers extensive features for large-scale applications.
3. File Server
File servers are designed to store and manage files, enabling users to share data over a network. These servers can host various types of files, including documents, images, videos, and software applications. File servers are essential in businesses and organizations, where multiple users need access to shared data in a centralized location.
Popular File Servers:
- Samba: An open-source software that allows file and print services for Windows clients on Linux and Unix servers.
- Microsoft Windows File Server: A file server solution integrated into Microsoft Windows Server, offering seamless file sharing across Windows environments.
- Nextcloud: An open-source platform for file sharing, similar to Dropbox, but with full control over the hosting environment.
4. Mail Server
Mail server software is responsible for sending, receiving, and storing email messages. Mail servers operate based on various email protocols, such as SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol), and POP3 (Post Office Protocol). These servers ensure reliable email communication, whether for personal use or enterprise needs.
Popular Mail Servers:
- Postfix: A fast and secure mail transfer agent (MTA) that routes and delivers electronic mail.
- Microsoft Exchange Server: A proprietary email and calendar server solution that integrates with other Microsoft services.
- Zimbra: An open-source collaboration suite that includes email, calendaring, and contact management.
- Sendmail: One of the oldest and most widely used email servers, offering robust email routing and management.
5. Application Server
Application servers provide the runtime environment needed for web applications and enterprise applications to run. These servers typically support the execution of specific application frameworks (e.g., Java, .NET) and handle tasks such as database connectivity, transaction management, and message routing.
Popular Application Servers:
- Apache Tomcat: An open-source Java-based application server that supports running Java Servlets and JavaServer Pages (JSP).
- JBoss (WildFly): A Java-based application server for deploying enterprise applications.
- GlassFish: An open-source application server for running Java EE (Enterprise Edition) applications.
- Microsoft IIS: Although primarily a web server, IIS also acts as an application server for ASP.NET applications.
6. DNS Server
DNS (Domain Name System) servers map domain names (e.g., www.example.com) to IP addresses, enabling browsers to find websites. DNS servers are essential for the functioning of the internet, as they provide the translation between human-readable domain names and machine-readable IP addresses.
Popular DNS Servers:
- BIND (Berkeley Internet Name Domain): The most commonly used DNS server on the internet, known for its flexibility and support for advanced DNS features.
- Unbound: A high-performance, open-source DNS resolver.
- Microsoft DNS: A DNS server solution integrated into Microsoft Windows Server environments.
How To Choose the Best Server Software?
When selecting server software for your organization or personal use, several factors need to be considered. The right choice will depend on the type of services you need to provide, the scale of your operations, and your existing infrastructure. Below are some important factors to keep in mind:
1. Operating System Compatibility
Ensure that the server software you choose is compatible with the operating system you plan to use. For example, NGINX and Apache work well on Linux-based servers, while Microsoft IIS is designed for Windows Server.
2. Performance and Scalability
Evaluate the performance capabilities of the software, especially if you expect high traffic or large amounts of data. Consider whether the software supports horizontal scaling (adding more servers) or vertical scaling (upgrading resources on a single server).
3. Security Features
Look for software with built-in security features to protect your system from unauthorized access. Features like SSL/TLS encryption, firewall integration, and authentication mechanisms are essential for protecting sensitive data and ensuring privacy.
4. Cost
While many server software options are open-source and free, others—especially enterprise-grade solutions like Microsoft SQL Server or Oracle Database—come with licensing costs. Factor in the cost of purchasing or subscribing to the software, as well as ongoing support and maintenance expenses.
5. Community and Support
Consider the level of community support or official customer service available for the software. Open-source solutions often have active communities and forums, while proprietary solutions offer official customer support and regular updates.
Setting Up and Configuring Server Software
Here is how you can set up and configure server software
1. Installation
The first step is to install the server software on your chosen server hardware. This process will vary depending on the software and operating system. Many server software solutions offer straightforward installation procedures or package managers (e.g., apt on Ubuntu, yum on CentOS) to make installation easy.
2. Configuration
Once installed, you’ll need to configure the server software to meet your specific needs. This may involve:
- Adjusting server settings (e.g., ports, server limits)
- Configuring user access and permissions
- Setting up network configurations
- Securing the server with firewalls, SSL certificates, and authentication mechanisms
3. Testing
After installation and configuration, it’s essential to test the server to ensure everything is functioning properly. Test connectivity, performance, and security to verify that the server is ready to handle client requests.
4. Maintenance
Server software requires regular updates and monitoring to ensure optimal performance and security. Set up monitoring tools to track server health, and regularly update the software to patch vulnerabilities.
Best Practices for Server Software Management
- Regular Updates: Always keep server software updated with the latest patches and security updates to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Backup: Regularly back up server data and configurations to avoid data loss in case of hardware failure or attacks.
- Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to track server performance, detect anomalies, and respond quickly to issues.
- Server Hardening: Secure your server by disabling unnecessary services, using firewalls, and employing strong authentication mechanisms.

Server Software
Conclusion
Server software is a critical component in today’s digital world, powering everything from websites and applications to email services and data storage. Choosing the right software, configuring it properly, and maintaining it over time are essential steps in ensuring your servers run smoothly and securely. By understanding the types of server software, the best practices for setup, and ongoing management, you can ensure that your server infrastructure is both reliable and high-performing.
Remember, managing server software is not a one-time task—it requires continuous monitoring, updates, and adjustments to meet changing demands. By staying up to date with the latest developments in server software and best practices, you’ll be well-equipped to handle any challenges that come your
Featured Post
Linux Mint vs Ubuntu: 10 Ultimate Comparison Points
Table of Contents Key Takeaways: Understanding Ubuntu Linux and Mint Linux Linux Mint vs Ubuntu: Are Linux and Ubuntu the Same? Linux Mint vs Ubuntu: Core […]
Dedicated Server For Government: Everything You Need to Know
In an era where digital transformation defines national competitiveness, governments around the world are investing heavily in resilient, secure, and scalable infrastructure. Among all infrastructure choices, […]
Dedicated Server with SSD: High-Performance Hosting for Mission-Critical Workloads
A Dedicated Server with SSD (Solid State Drive) is a premium hosting solution in which an entire physical server is allocated to a single user and […]